The exchange pattern
Intent
Creation of a smart contract where 1 instance of the smart contract will allow for an arbitrary amount of trades, where each trade is an exchange between 2 entities.
Consequences
- There are an arbitrary amount of traders that can all trade with one another.
- The smart contract is able to run indefinitely.
Structure
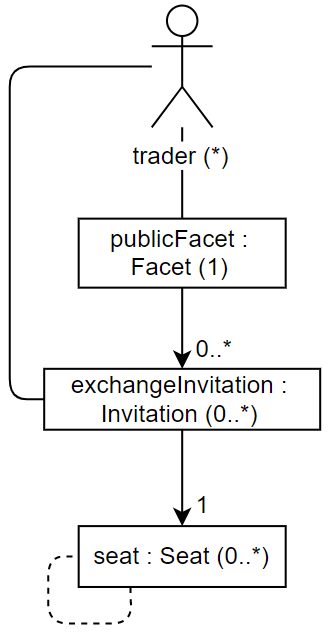
Participants
- Trader: the entity that wants to trade something.
Implementation
const start = zcf => {
const seats = /*some data structure*/;
const exchangeOfferHandler = seat => {
//look for matching seat in seats with matching algorithm
//IF match found THEN trade ELSE add seat to seats
};
const publicFacet = Far('publicFacet', {
makeInvitation: () => zcf.makeInvitation(exchangeOfferHandler, 'exchange')
});
return harden({ publicFacet });
};
harden(start);
export { start };
The smart contract stores a collection of seats in some kind of data
structure. The smart contract returns a publicFacet with a method
exchangeInvitation. The offer handler linked to this
exchangeInvitation will look for a seat in the collection of seats
that satisfies the proposal. This is done using some kind of matching
algorithm. If a matching seat is found, then the trade is executed. If
no such seat is found, then the seat is added to the collection of seats
in the smart contract. This allows the seat to be included in future
searches performed by the matching algorithm.
Known uses
- The barter exchange smart contract.
- The simple exchange smart contract.
Related patterns
- The independent participation pattern: since the exchange pattern
provides a
publicFacetwith a method to create invitations, it can be stated that the exchange pattern makes use of the independent participation pattern. - The salesperson pattern: both the salesperson pattern and the exchange pattern are able to run indefinitely. The difference is that in the exchange pattern, an arbitrary amount of traders will trade with one another, while in the salesperson pattern, an arbitrary amount of customers will trade with a single creator.